- Blog /
- How to Decommission a vmstorage Node from a VictoriaMetrics Cluster
How to Decommission a vmstorage Node from a VictoriaMetrics Cluster
Problem
#
We need to remove a vmstorage node from VictoriaMetrics cluster gracefully. Every vmstorage node contains its own portion of data and removing the vmstorage node from the cluster creates gaps in the graph (because replication is out of scope).
Setup example
#
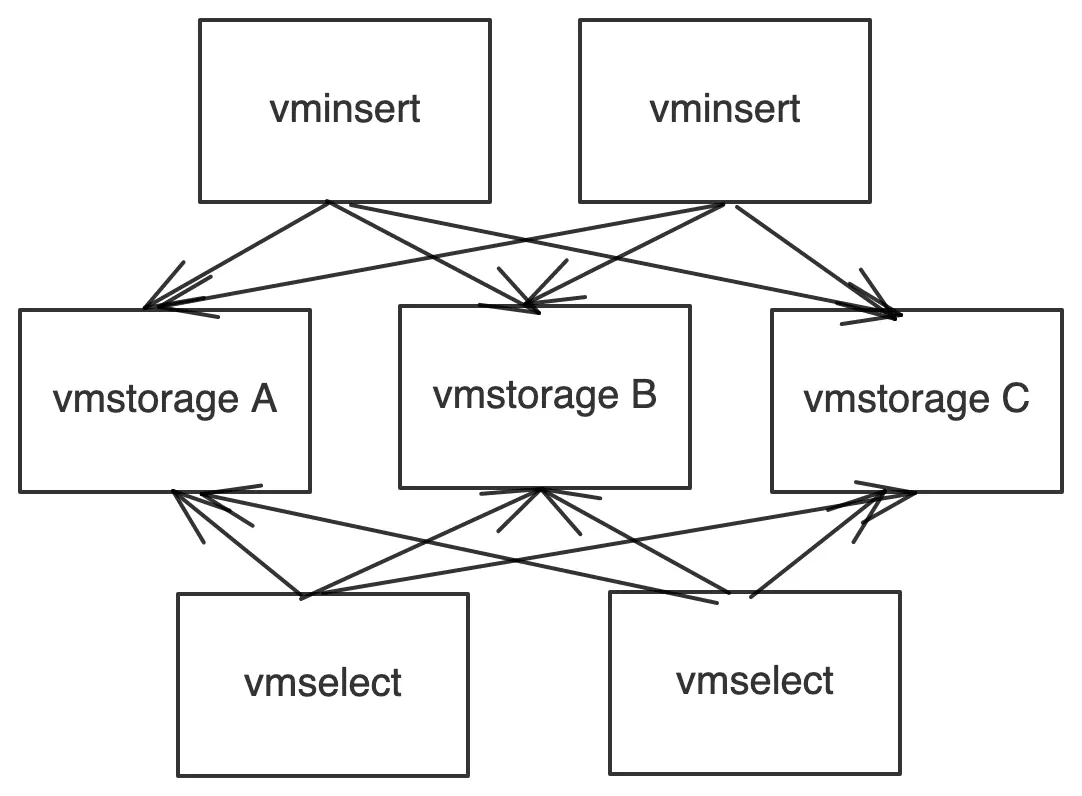
We have a VictoriaMetrics cluster with 2 vminsert, 2 vmselect and 3 vmstorage nodes. We want to gracefully remove vmstorage A from the cluster.
Solution One
#
- Remove
vmstorage Afrom the vminsert list - Wait for the retention period
- Remove
vmstorage Afrom the cluster
Note: please expect higher resource usage on the existing vmstorage nodes (vmstorage B and vmstorage C), as they now need to handle all the incoming data.
Pros: Simple implementation
Cons: You may need to wait for a long period of time
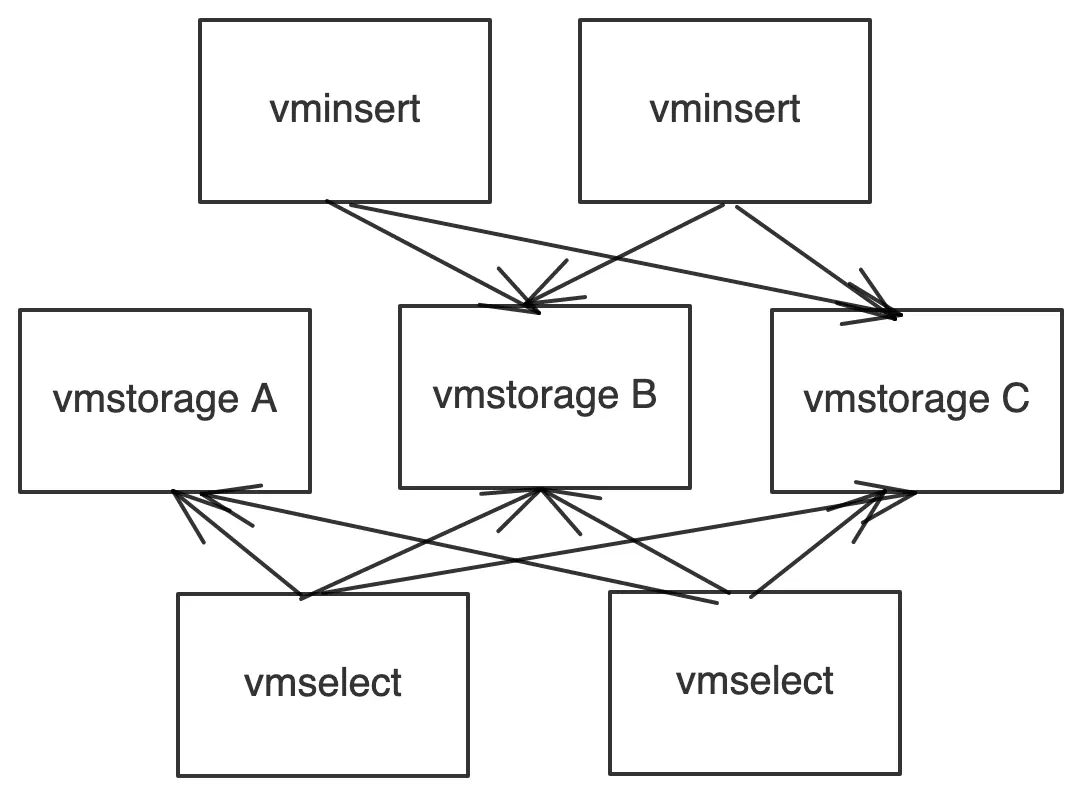
Solution Two
#
- Remove
vmstorage Afrom the vminsert list (same as in Solution One). - Set up a dedicated vmselect node that knows only about the vmstorage node that we want to remove (vmstorage A). We need this vmselect node for migration data from vmstorage A to other vmstorage nodes in the cluster.
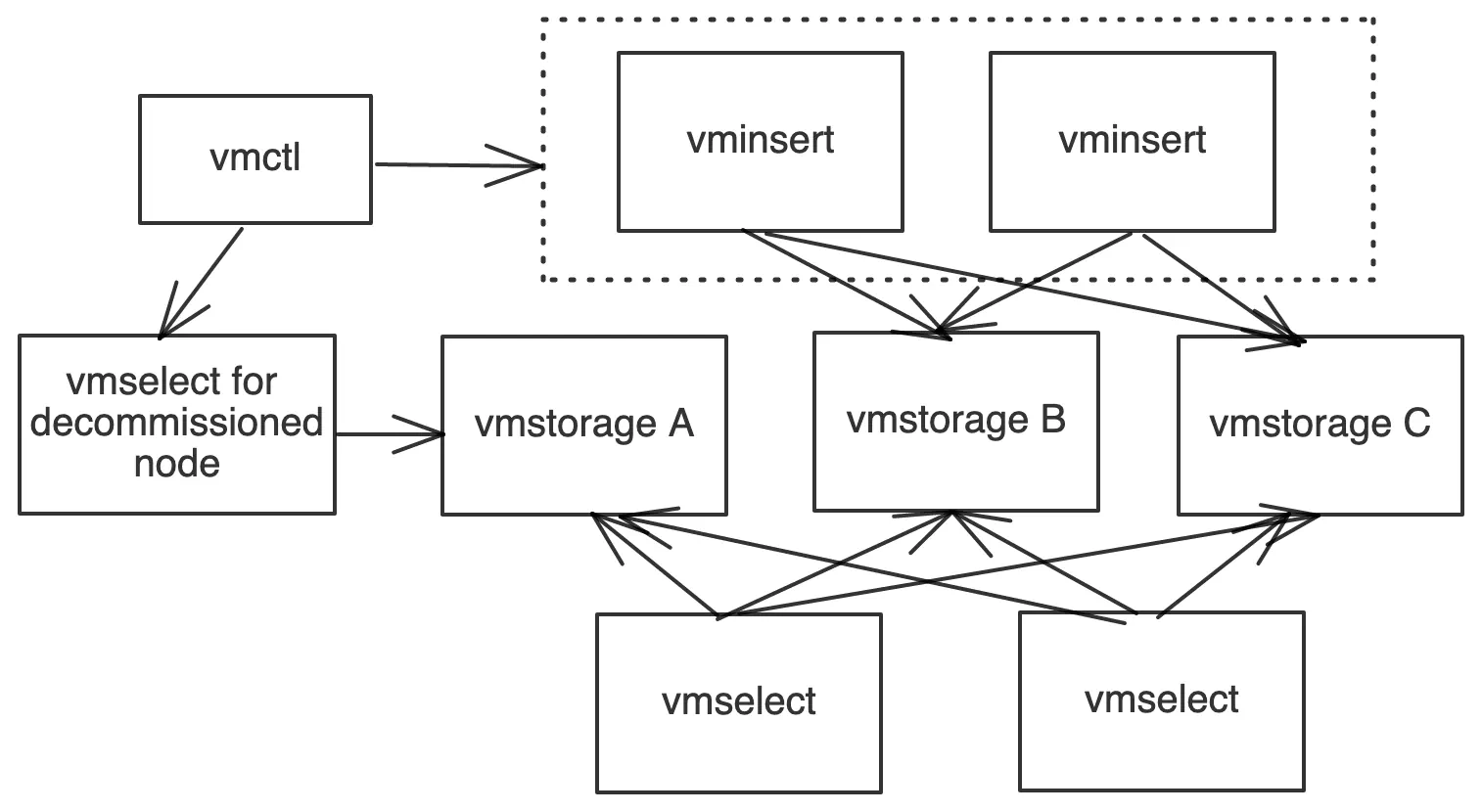
- Using vmctl native import/export reads data from vmselect for
vmstorage Aand writes data back to vminsert nodes. 4. This process creates duplicates. - Turn on deduplication on vmselect nodes.
- Remove
vmstorage Afrom the cluster.
Note: Please expect higher resource usage on the existing nodes (vmstorage B and vmstorage C), as they now need to handle all the incoming data.
Pros: Faster way to decommission a vmstorage node.
Cons: The process is more complex compared to solution One. The vmctl import/export process may require tuning if you migrate hundreds GB of data (or more).
Hint : downsampling reduces the amount of data in a cluster; after downsampling, the vmctl migration requires less data to transfer and less time.
We trust that this is helpful!
Please let us know how you get on or if you have any questions by submitting a comment below.
Leave a comment below or Contact Us if you have any questions!
comments powered by Disqus